11. Present Values#
11.1. Overview#
This lecture describes the present value model that is a starting point of much asset pricing theory.
Asset pricing theory is a component of theories about many economic decisions including
consumption
labor supply
education choice
demand for money
In asset pricing theory, and in economic dynamics more generally, a basic topic is the relationship among different time series.
A time series is a sequence indexed by time.
In this lecture, we’ll represent a sequence as a vector.
So our analysis will typically boil down to studying relationships among vectors.
Our main tools in this lecture will be
matrix multiplication, and
matrix inversion.
We’ll use the calculations described here in subsequent lectures, including consumption smoothing, equalizing difference model, and monetarist theory of price levels.
Let’s dive in.
11.2. Analysis#
Let
We assume that the dividend stream
This means that they are determined outside the model.
Assume the sequence of asset pricing equations
We say equations, plural, because there are
Equations (11.1) assert that price paid to purchase the asset at time
Discounting tomorrow’s price by multiplying it by
We want to solve the system of
A system of equations like (11.1) is an example of a linear difference equation.
There are powerful mathematical methods available for solving such systems and they are well worth studying in their own right, being the foundation for the analysis of many interesting economic models.
For an example, see Samuelson multiplier-accelerator
In this lecture, we’ll solve system (11.1) using matrix multiplication and matrix inversion, basic tools from linear algebra introduced in linear equations and matrix algebra.
We will use the following imports
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
11.3. Representing sequences as vectors#
The equations in system (11.1) can be arranged as follows:
Write the system (11.2) of
Exercise 11.1
Carry out the matrix multiplication in (11.3) by hand and confirm that you recover the equations in (11.2).
In vector-matrix notation, we can write system (11.3) as
Here
The solution for the vector of prices is
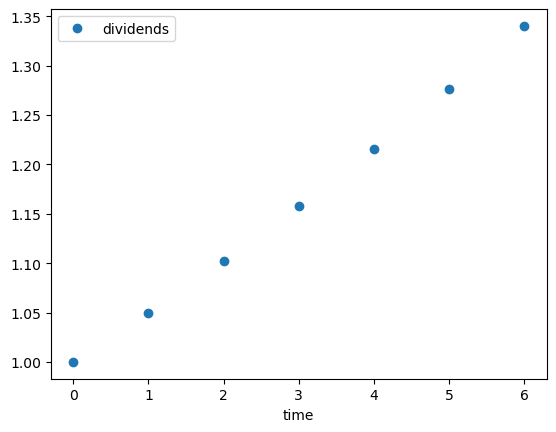
For example, suppose that the dividend stream is
Let’s write Python code to compute and plot the dividend stream.
T = 6
current_d = 1.0
d = []
for t in range(T+1):
d.append(current_d)
current_d = current_d * 1.05
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot(d, 'o', label='dividends')
ax.legend()
ax.set_xlabel('time')
plt.show()
Now let’s compute and plot the asset price.
We set
δ = 0.99
p_star = 10.0
Let’s build the matrix
A = np.zeros((T+1, T+1))
for i in range(T+1):
for j in range(T+1):
if i == j:
A[i, j] = 1
if j < T:
A[i, j+1] = -δ
Let’s inspect
A
array([[ 1. , -0.99, 0. , 0. , 0. , 0. , 0. ],
[ 0. , 1. , -0.99, 0. , 0. , 0. , 0. ],
[ 0. , 0. , 1. , -0.99, 0. , 0. , 0. ],
[ 0. , 0. , 0. , 1. , -0.99, 0. , 0. ],
[ 0. , 0. , 0. , 0. , 1. , -0.99, 0. ],
[ 0. , 0. , 0. , 0. , 0. , 1. , -0.99],
[ 0. , 0. , 0. , 0. , 0. , 0. , 1. ]])
Now let’s solve for prices using (11.5).
b = np.zeros(T+1)
b[-1] = δ * p_star
p = np.linalg.solve(A, d + b)
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot(p, 'o', label='asset price')
ax.legend()
ax.set_xlabel('time')
plt.show()
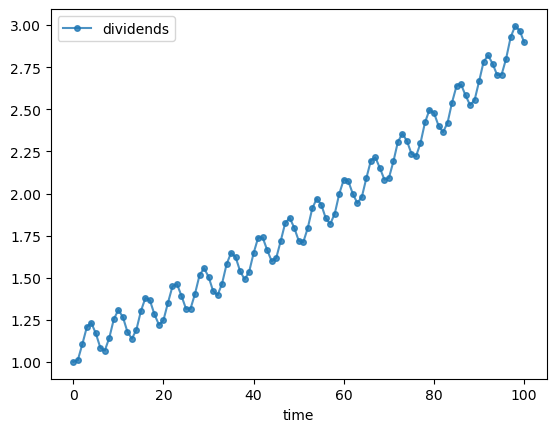
Now let’s consider a cyclically growing dividend sequence:
T = 100
current_d = 1.0
d = []
for t in range(T+1):
d.append(current_d)
current_d = current_d * 1.01 + 0.1 * np.sin(t)
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot(d, 'o-', ms=4, alpha=0.8, label='dividends')
ax.legend()
ax.set_xlabel('time')
plt.show()
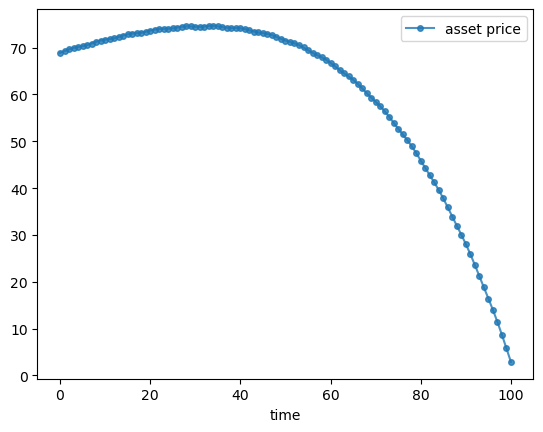
Exercise 11.2
Compute the corresponding asset price sequence when
Solution to Exercise 11.2
We proceed as above after modifying parameters and consequently the matrix
δ = 0.98
p_star = 0.0
A = np.zeros((T+1, T+1))
for i in range(T+1):
for j in range(T+1):
if i == j:
A[i, j] = 1
if j < T:
A[i, j+1] = -δ
b = np.zeros(T+1)
b[-1] = δ * p_star
p = np.linalg.solve(A, d + b)
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot(p, 'o-', ms=4, alpha=0.8, label='asset price')
ax.legend()
ax.set_xlabel('time')
plt.show()
The weighted averaging associated with the present value calculation largely eliminates the cycles.
11.4. Analytical expressions#
By the inverse matrix theorem, a matrix
It can be verified that the inverse of the matrix
Exercise 11.3
Check this by showing that
If we use the expression (11.6) in (11.5) and perform the indicated matrix multiplication, we shall find that
Pricing formula (11.7) asserts that two components sum to the asset price
a fundamental component
a bubble component
The fundamental component is pinned down by the discount factor
The bubble component is the part of the price that is not pinned down by fundamentals.
It is sometimes convenient to rewrite the bubble component as
where
11.5. More about bubbles#
For a few moments, let’s focus on the special case of an asset that never pays dividends, in which case
In this case system (11.1) of our
Evidently, if
But let’s activate the bubble component by setting
for some positive constant
In this case, when we multiply both sides of (11.8) by
the matrix
11.6. Gross rate of return#
Define the gross rate of return on holding the asset from period
Substituting equation (11.10) into equation (11.11) confirms that an asset whose sole source of value is a bubble earns a gross rate of return
11.7. Exercises#
Exercise 11.4
Assume that
Solution to Exercise 11.4
Plugging each of the above